Electricity Scenario of the state of Andhra Pradesh
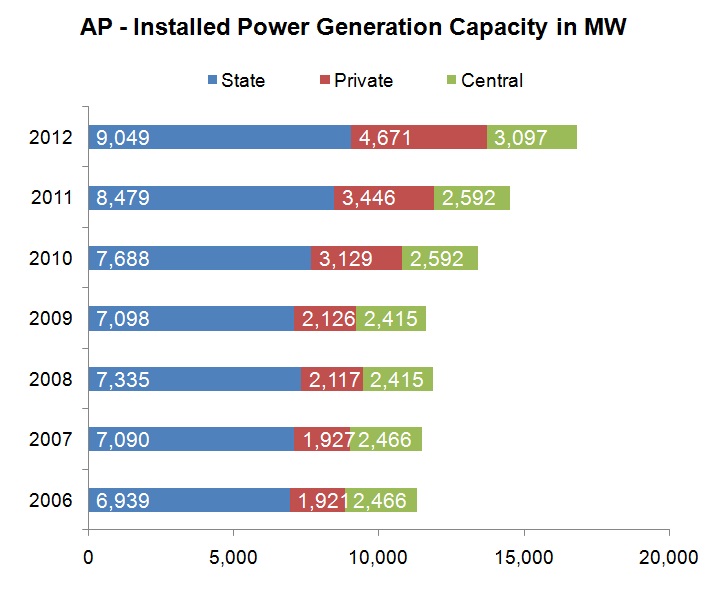 The state of Andhra Pradesh (AP) is located in the southern part of India and forms a major constituent of the southern grid. Major electricity generation happens through the thermal and the hydro power plants. These power plants are being operated by Andhra Pradesh Power Generation Company (APGENCO). By Feb 2013, Andhra Pradesh is the fourth largest power generating state in the country and also has the largest hydro power generation capacity in India (Andhra Pradesh is on first position for installed hydro power generation capacity). At present, Andhra Pradesh has a total installed power generation capacity of 16,817 MW from all the sources. Out of it, 11771 MW is from thermal, 3737 MW is from Hydro, 1036 MW is from Renewable energy sources and 276 MW is from Nuclear (CEA- Dec 2012).
The state of Andhra Pradesh (AP) is located in the southern part of India and forms a major constituent of the southern grid. Major electricity generation happens through the thermal and the hydro power plants. These power plants are being operated by Andhra Pradesh Power Generation Company (APGENCO). By Feb 2013, Andhra Pradesh is the fourth largest power generating state in the country and also has the largest hydro power generation capacity in India (Andhra Pradesh is on first position for installed hydro power generation capacity). At present, Andhra Pradesh has a total installed power generation capacity of 16,817 MW from all the sources. Out of it, 11771 MW is from thermal, 3737 MW is from Hydro, 1036 MW is from Renewable energy sources and 276 MW is from Nuclear (CEA- Dec 2012).
Apart from the state sector, private players have considerable presence in Andhra Pradesh. Private power plants operating in the state use transmission lines of Andhra Pradesh Transmission Company (AP Transco) that looks after the trans-mission of electricity in the state. Due to its geographical location, the power generated by all power plants is being fed to the Southern Grid, which is accessible to all states which are a part of the southern grid.
Central sector owned power plants operated by National Thermal Power Corporation (NTPC), National Hydro Power Corporation (NHPC), etc transmit power through transmission lines of AP Transco. However, the power generated by them is shared between other states as a part of the southern grid of India.
Institutional structure of Electricity sector in AP
Basically, institutional structure of the electricity sector can be categorized into four main domains i.e. Regulation, Generation, Transmission and Distribution. In Andhra Pradesh, APERC look after regulation related matters, APGENCO is engaged in power generation, APTRANCO is mainly responsible for transmission and there are four electricity distribution companies as mentioned in the following figure;

Power-Supply position of Andhra Pradesh
Andhra Pradesh has experienced increasing capacity addition in the last few years. To meet the expanding energy requirement in the state, additions to generating capacity were made, expected to leading in reducing deficits. However, the state of Andhra Pradesh has been experiencing increasing energy deficits since 2004-05.
In spite of additional installed capacity, peak demand deficit in the state has increased from 2% in 2005-06 to15% in 2011-12. Between 2005-06 and 2011-12, Peak electricity demand grew at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8%, while peak demand met at CAGR of 6% over the period of 8 years.

Electricity deficit in the state has increased from a negligible 1% in 2005-06 to 7% in 2011-12. The reason for the increasing deficits can be mainly traced to the inability of the state to increase electricity generation. Between 2005-06 and 2011-12, electricity requirement grew at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8%, while availability only grew at around 7% leading to increasing electricity deficits.

The above data shows that the electricity availability against the demand is low and the deficit is increasing in each year. It is expected that the power deficit post 2012 will continue to increase as the demand for power is continuously surpassing supply.
Power shortage is getting worse in the state
Despite the discovery of natural gas in Krishna Godavari basin (KG-Basin), natural gas based power plants established near costal part of Andhra Pradesh are running on minimum plant load factors due to lower gas production. Generation in hydro power units has also come down due to low water levels in the reservoirs resulted by seasonal variability of monsoon.
Under these circumstances, power utilities are forced to impose power supply rationing. Major and medium industries in Andhra Pradesh experience increasing number of “power holidays” as the state power distribution companies are unable to meet the growing demand for electricity.
The prolonged electricity shortage is unfavorable for the overall development of the state. Industries are adversely affected and have started relying on expensive power from the DG sets. The increasing price of diesel is also a big concern for them.
Any development requires electricity to support it. Capacity addition in the existing conventional power generation plants might not be the solution. We need fuel to run them. The Government of India has started promoting increasing use of renewable energy in the total energy mix. Renewable energy cannot solve this issue completely but can surely help to overcome it.
Let’s hope for a better policy from the government to promote renewable energy.
References: Central Electricity Authority (CEA), APGENCO, APERC
Read more on – Summary of Incentives and Subsidies for Renewable Energy Products by MNRE
Read more on Top Five States in India with Highest Renewable Energy Capacity and Top five states in India with highest installed electricity generation capacity.


nice work.important information at one place.congratulations
Thanks for your comment. Stay tuned with us for more details on the same topic.
sorry to say this but upto 2010 our production of power is more than demand……..but you are showing deficit….. whats the reason behind it
Thanks for your comment Mr. Chandra Sekhar. The data used in the analysis is sourced from Central Electricity Authority (CEA) website which is a supreme government body for electricity related information. I haven’t used any of information used in this post from any other source. You can also check it from CEA website. If you still believe that the information mentioned in the post is wrong, please send your source(s) of the information on shailesh(at)greencleanguide(dot).com.
you can refer official sites of electricity department for clear idea
nice information it will be better if you can show the details in numbers of the power produced from various sources in AP and the usage of power and shortage in numbers
Thanks for your comment. We will try to do it.
can we get 2013 data please ……..its very urgent
State: 9050.06 MW, Private: 4968.06 MW, Central: 3156.76 MW. (as on Sep 2013)
shailesh …….if you dnt mind …..can you please answer my q
1.what is the present production of power in andhra pradesh
2.what is the demand of the power in andhra pradesh
3.what is the supply of the power in andhra pradesh
4.can we get the power allocation by regions and dists ? where do i get that information
From the beginning of this financial year, i.e. from April 2013 till Aug 2013, Electricity generation in the state of AP was 36,019 Million units however, requirement was 40,524 (11.1% deficit). From April 2013 till July 2013; peak power demand in AP was 14,072 MW, However, only 11,410 MW was met through existing capacity and open access mechanism (which means, 18.9% of deficit). Data on power allocation by region in AP is not available. However, you can always search for different sources for the same.
For more information visit APGENCO/CEA websites.
If you dnt mind……….tell me about losses i mean T&D(transmission & distribution losses)& Commerical losses % in present generation.