Electricity scenario of the state of Gujarat
 The Indian power sector is facing challenges despite the significant growth in generation capacity over the past few decades. The power situation in India is characterized by demand in excess of supply, high transmission and distribution losses, peak demand and energy shortages, low plant load factors, and decreasing availability of best quality fuel to run the power plants. However, over the last few years, Gujarat has successfully crossed all these barriers. Gujarat has become successful in securing its overall energy requirements with an installed power generation capacity of 23,927 MW (as of Aug 2012).
The Indian power sector is facing challenges despite the significant growth in generation capacity over the past few decades. The power situation in India is characterized by demand in excess of supply, high transmission and distribution losses, peak demand and energy shortages, low plant load factors, and decreasing availability of best quality fuel to run the power plants. However, over the last few years, Gujarat has successfully crossed all these barriers. Gujarat has become successful in securing its overall energy requirements with an installed power generation capacity of 23,927 MW (as of Aug 2012).
The institutional structure of the power sector in Gujarat
In the year 1999, the state of Gujarat established the Gujarat Urja Vikas Nigam Limited (GUVNL) under the Companies Act, 1956. The GUVNL was created by the Gujarat Electricity Board (GEB) as its wholly-owned subsidiary towards restructuring of the power sector for better management. GUVNL was incorporated as a Government of Gujarat Company which holds 100% of shares in the other six companies i.e. Gujarat State Electricity Corporation Limited(GSECL), Gujarat Energy Transmission Corporation Limited GETCO), Uttar Gujarat Vij Company Limited (UGVCL), Dakshin Gujarat Vij Company Limited (DGVCL), Madhya Gujarat Vij Company Limited (MGVCL) and Paschim Gujarat Vij Company Limited (PGVCL).

All six companies are 100% subsidiaries of GUVNL. The GUVNL is engaged in Supervision, Co-ordination, and facilitation of the activities of its six Subsidiary Companies.
Power supply-demand position in Gujarat
As a result of growing installed power generation capacity, the peak demand-peak deficit in the state has decreased by the Compound Annual Growth Rate of 31%.

The actual power supply position of the state of Gujarat has improved in the last seven years considerably. The power requirement and availability deficit in the state have been decreased by a CAGR of 38%. The year 2012 shows nearly zero percent deficit made Gujarat power sufficient.

Renewable energy scenario in Gujarat
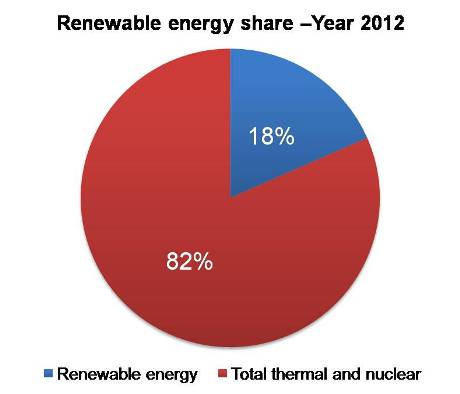 Gujarat is rich in solar energy, biomass, and wind energy. It is also the leading state in terms of overall solar energy installation in India. As part of its renewable energy promotion policy, Gujarat enacted the country’s first Wind Energy policy in 1993 and become the first state with a Solar Policy in 2009. As per the Gujarat Energy Development Agency (GEDA), the state has tremendous renewable energy potential;
Gujarat is rich in solar energy, biomass, and wind energy. It is also the leading state in terms of overall solar energy installation in India. As part of its renewable energy promotion policy, Gujarat enacted the country’s first Wind Energy policy in 1993 and become the first state with a Solar Policy in 2009. As per the Gujarat Energy Development Agency (GEDA), the state has tremendous renewable energy potential;
Table showing renewable energy potential of the state of Gujarat;
| Source | Resource | Energy Generation/Saving Potential |
| Solar | Solar Radiation 300 days | 5.6 -6.0 kwh/m2/ day |
| Biomass | 24 million tones | 900 MW of electric power could be generated to meet energy requirements of almost all villages in Gujarat. |
| Biogas | 200 lakh cattle population (Dung available at 70% collection efficiency) |
Could generate 5.6 million cubic meter of biogas per day to cater cooking gas to 2.8 million families or generate electric power equivalent to 933 MW |
| Biogas Energy Plantation |
67 lakh hectare wasteland | Could yield 67 million tones of Biomass which can sustain power generation to the order of 15000 MW |
| Wind | The coastline and hilly regions | 5000 MWe |
| Tidal | Gulf of Kachchh Gulf of Khambhat |
9000 MWe 9000 MWe |
The economics time quoted, “Gujarat’s overall integrated renewable energy potential is estimated to be around 748.77 GW. A study conducted by TERI, Gujarat’s potential for concentrated solar power (CSP) with water availability stands at 345.71 GW, solar photovoltaic (SPV) wind hybrid excluding CSP at 240.60 GW, only SPV excluding wind and CSP at 21.36 GW, only wind excluding solar potential at 139.21 GW and biomass at 1.89 GW.” (ET, 20 April 2012).
Increasing power generation capacity in each year along with the growing share of Renewable energy in its total energy mix has made Gujarat a prominent destination for investment. Gujarat government is positively looking towards renewable energy which reduces dependency on conventional fuel. Let’s hope for a similar model in other parts of the country.
Please click here to view the list of solar power plant commissioned in Gujarat.
Need more information on solar energy development in Gujarat? Please click here.
Read more on Summary of Incentives and Subsidies for Renewable Energy Products by MNRE.


Wind energy is seasonal. Solar can go off for a few days in a year due to monsoon clouds. Tidal is not yet a proven &
dependable source of energy. Is Gujarat’s lignite potency being fully used. Its waste lands can be utilised for large scale planting of cashurina/eucliptus or other fast growing trees. Within 5 to 7 years, the trees can be cut and used as fuel in thermal power stations.
Thanks for your comment. Renewable energy like wind and solar is though seasonal but can contribute considerably in the overall energy mix and also help to greenhouse gas emission reduction. Having major energy portion from conventional and some (possible) portion from renewables always help to utilize optimum energy potential from these sources. In addition, growing biomass on wasteland and further its utilization for energy generation is also a best possible option in near future. Solar Power Policy (2009) introduced by GEDA, Govt of Gujarat clearly mentioned “Productive use of the wastelands, thereby engendering a socio economic transformation”. Please read relevant articles here http://greencleanguide.com/2011/05/08/the-sun-is-bright-in-gujarat/ and http://greencleanguide.com/2011/01/18/wastelands-types-and-status-in-india/
In reference to the data shown above i have few question..
1).Considering present condition of Gujarat which Renewable Energy Source (RES) can be promoted for Future needs and why?
2).If there was no RES in Gujarat which conventional energy can be promoted and why?
Comment on your first question;
Both wind and solar energy projects are suitable on Gujarat soil. However, project developers may prefer solar projects from this year. Before March 31, 2012, wind energy project developer was eligible to take accelerated depreciation (AD) benefits. Now the same has been transferred to solar energy projects and this could be the reason behind inclination towards solar projects.
In addition, tariff for the power purchased by utility/others from solar and wind energy projects is different – Solar (Levelized Tariff for 25 years is Rs 9.28/kWh for project availing AD and Rs. 10.37/kWh for projects not availing AD + With 7% decline in FY14 and FY 15 respectively) and Wind (4.23 Rs./KWh). Source: GERC 2012 tariff orders for solar and wind.
Technically, wind energy projects can give around 22-28% of PLF depends on site and solar can come up around 14-22% depends on the type of technology (Solar PV and CSP).
Other RES like biomass and hydro can come up depends on resource availability.
Comment on your second question:
Probably coal and natural gas would be the best options for conventional power generation.
For meeting the energy demand of Gujarat wat is the (approx) amount of Coal(in Tonnes per day or per year), Lignite(Tonnes per day or percyear), Oil(Barrels or Lits per day or per year), Natural gas(Cubic Meter per day or year) being used??
It seems like you are in need of data for your college project or assignment. I suggest to visit Ministry of Petroleum, Ministry of Coal and Ministry of Power websites. You can also check various report on “Indian electricity sector” by planning commission of India (It’s available on their web site). Gujarat government also provide good information on their respective official websites.
thanx for the suggestion… i did check the site, n have also found the details to an extent. As soon as my report for Gujarat gets ready i will be happy to send it to u as a token of gratitude for ur help…
n the report was not for my collage assignment or project… it was for my own research, since in my collage wen ever m asked about my state for the status of electricity or power consumption i dint hav a solid shot report n an answer so i thought of makin it…. 🙂
That’s great Tarun. Please share your short report with us. We will help you in every possible aspect of your research.
Thanx a lot… for ur ans n time…
Hey guys , this is a good discussion going on here.. well Shailesh and Tarun could you share your details with me what do you do and where do you study ? my email address in parthpatel_28@hotmail.com. I am also studying in this field. would like to hear from you.
thanks 🙂
Hi Parth,
Thanks for commenting here.
Please visit my profile here http://greencleanguide.com/team/
Please do subscribe to our website via email and also like us on facebook to receive each new updates on GreenCleanGuide.com.
give me your report….plz
Hi,
Thanks for commenting. What kind of report you want? Please come up with specific requirements.
i want report of convention and renewable status of india…
thought I am more on sustainable energy side..
why coal and natural gas would be the best options for conventional power generation in gujarat…can u plz rpy me …its urgent
In India, the contribution of Renewable energy is limited. In addition, it can support overall energy requirement but cannot displace conventional energy resources completely. We have more than 60% of total installed electricity generation capacity on coal and other fossil fuel based power sources. We have considerable coal reserves too. Therefore to support growing energy need, coal and natural gas might be the best options for conventional power generation.
Can u please answer my questions :-
1- Most abundant form of electricity used in Gujarat
2- The uses of different form of electricity in the sectors of agriculture,industry,transport and domestic household.
3- Role of electricity in the development of the state in general
what about hydroelectricity in Gujarat?
can i get the amount of power consumption in gujarat. all types of power as a whole
what are the major problems faced by Gujarat in energy sector currently and what are its solutions? Can you please revert back asap its urgent