World Zoonoses Day Assumes More Significance in Today’s World
Every year, on 6 July, World Zoonoses Day is celebrated. This day commemorates Louis Pasteur and his role in administering the first successful vaccine against Rabies virus back in 1885.
Infectious diseases that are caused by virus, parasite, fungi or bacteria, and spread from animals to humans (or vice-versa) are termed zoonotic diseases. These can spread either from direct contact or indirectly, such as through vectors or food.
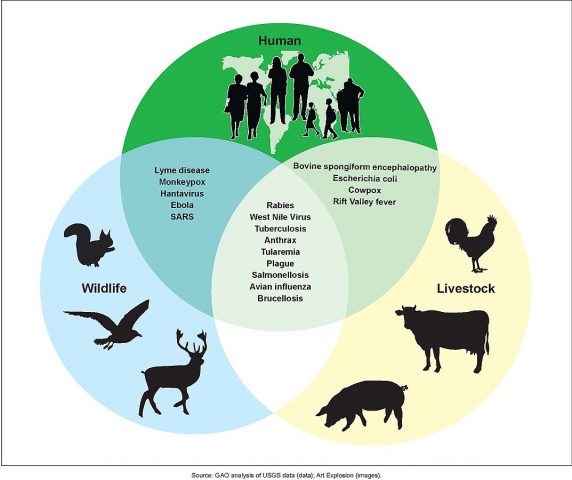
Below are listed various zoonotic diseases, causes and whether or not vaccine is available for treatment.
| Zoonotic Disease | Cause of Disease | Vaccine |
| Anthrax | Bacillus anthracis bacteria | AVA |
| Bird Flu | Influenza virus, H5N1 & H7N9 | None |
| Dengue fever | Dengue virus | Denvaxia (CYD-TDV) |
| Hepatitis E | Hepatitis E virus | HEV 239 vaccine, Hecolin |
| Malaria | Plasmodium parasite | Mosquirix |
| Plague | Yersinia pestis bacteria | None |
| Swine Flu | Influenza virus | Pandemrix and Celvapan |
| Salmonella and E.coli infection | Salmonella bacteria | Ty21a |
| Rat-bite fever | Streptobacillus moniliformis, Spirillum minus bacteria | Penicillin G |
| Covid-19 | Coronavirus | None |
In the light of spread of Covid-19, what gains utmost importance is isolation from animals that may act as vectors of disease. For this reason, purposefully, our ancestors preferred domesticating cats and dogs for comfort, as well as protection, instead of animals like pigs. Diseases from these canine and feline companions are very difficult or cannot transmit to humans. Even for consumption, people would avoid eating rodents or creatures that lived on filth.
Today, when the world reels under this pandemic, it is more than necessary to understand what should stay on our plate and what not. Maintaining proper distance or completely avoiding animals that help spread zoonotic diseases is key to survival. Healthy diet plays a crucial role in helping develop our immune system and assisting it to fight off any infection. Thus, consuming foods rich in immunity boosters should be our priority.
Include citrus fruits, broccoli, garlic, spinach, almonds, red bell peppers, and yogurt in your diet. Avoid deep fried or oil-based stuff. Also make sure you eat at home most of the time. It is better to cook than order food from restaurants or food chains nowadays. As frequently as you can, drink lots of water too.
Tips to Avoid Zoonotic Infection
The most basic tip is awareness. Read and be aware of the causal agents of zoonotic diseases. Make sure to completely understand where and when the risk of exposure is maximum. To know more, consult genuine books and research papers. You can even visit your neighbourhood physician for details and preventive measures. Households with children and elderly need to be even more cautious.
In addition to being aware, follow the pointers listed below:
- Avoid bites or scratches from animals
- Limit consuming pork or rodent meat
- To prevent mosquito, tick or flea bites, use protective clothing
- Hand hygiene, washing hands with soap, cleaning with sanitizers, should not be neglected
- Store and handle food safely
- When cooking meat or vegetables, make sure to wash and steam properly
- Use of masks when going out in public places
- Take your pets for regular annual visits to the veterinarian and have them vaccinated
- Don’t drink, eat or touch your face when in close contact with animals
- Keep the animal area sanitary
- Keep away from sick animals, both at home or in the wild, if you aren’t aware about handling them
- Make sure to keeps ticks or fleas away from your house. Home hygiene is important too.
More transmission occurs when people are on a hike, camping, riding bikes or enjoying outdoor activities. So, it is important to take proper precautions when going out. Many zoonotic diseases can, although, be cured but there are some strains that develop due to microbe mutation, unfortunately much deadlier than their predecessor. Therefore, it is always reasonable to avoid foods and/or places where risk of exposure may increase.
Stay safe!

