Common Bird Monitoring of India – A short report on the 4 common bird species in India
Common Bird Monitoring of India (CBMI) is a Citizen Science Program of Nature Forever Society (NFS). It is a first-of-its-kind national project that aims to monitor 18 common birds of the country. Citizen science projects are very recent phenomena in India and before us, no other conservation program for common birds of such national scale existed.
CBMI was launched on the occasion of World Sparrow Day in 2012. As on 19th March 2014, we have 2301 registrants from 34 states/UTs and 3 countries from the Indian subcontinent. According to the data from last two years on CBMI, House Sparrow (Passer domesticus) is the fourth most common bird species. House Sparrow, once the most common ubiquitous species in urban habitats all over India is now at number four.
The numbers are given in terms of the number of sightings. As can be well-imagined, Rock Pigeon (Columba livia) with 27064 sightings is the most commonly found bird across India followed closely by House Crows (Corvus splendens) with 26707 sightings while Common Myna (Acridotheres tristis) is the third most common species with 21398 sightings.
The population of Pigeons and Crows have remarkably shot up in the past decade or so. These can be correlated with the following points:
- In comparison to the sparrows, pigeons are having a gala time, specially in metros like Mumbai and Delhi where you have commercial Kabutarkhanas (feeding grounds) which offer grains in tons like Jowar or Black Gram to the pigeons. This has resulted in large scale feeding centers which are operated for commercial reasons targeting morning joggers, tourists or people with religious feeding. Some of the major kabutarkhanas are near tourist places, like Gateway of India, Marine Drive, CST or near religious places like temples, mosques/dargahs etc. With an assured source of food available every day, one has observed an exponential rate of population increase in birds like Pigeons in recent times.
- When you compare with sparrows, pigeons do not have to worry about feeding their young ones as the free food they get from the kabutarkhanas is easily converted into vegetable milk which is high in protein content by simple regurgitation of the free food they get from the Kabutarkhanas. On the other hand, the young ones of sparrows require an exclusive insect or protein food in their first 16 days due to their high metabolic rate and need to grow fast. In recent times, there has been a marked decline of insect food due to decline of native plants, the lack of insect food has resulted in increase of mortality of house sparrows chicks.
- In urban locations, the natural predators of birds such as pigeons have declined sharply. This has in turn lead to un-controlled growth in the number of pigeons due to lack of predators, they are growing at an exponential rate. While sparrows are preyed upon by a number of predators including crows, and also domesticated feral cats that prey on Sparrows.
- Besides, pigeons and crows do not need cavities to nest. They can nest on flat surfaces easily; you can easily find pigeon nests above AC’s, ceilings and even behind refrigerators. This is not the case for Sparrows. Due to the change in architectural design of homes, offices and other buildings, there aren’t even cavities left for Sparrows to find nesting spaces.
- Crows are one of the most efficient scavengers of all bird species. In a city like Mumbai, thanks to an inefficient garbage disposal system, food is always available for this clever scavenger. Apart from this, the open air illegal eateries spread across the length and breadth of Mumbai provide a constant source of food for the crows. Another source of food is the slaughter house, fish markets. It is interesting and fascinating to watch these clever birds riding on the top of taxis where fish baskets are kept by the fish sellers stealing a Bombay Duct or a prawn. The constant food availability for these birds results in an ever increasing population of crows in cities like Mumbai. However, in cities where so much garbage and free food is not available, you will notice that the crows are either in their natural numbers or in some places there is also a local decline observed in crows population.
- Besides, the decline in the population of owls and other predators in urban areas have lead to uncontrolled population growth of crows.
- Common Myna has been named as world’s most invasive species. Its wide range of eating habits, its high adaptability to human habitations and aggressive nature has led to its increasing spread in the last decade or so.
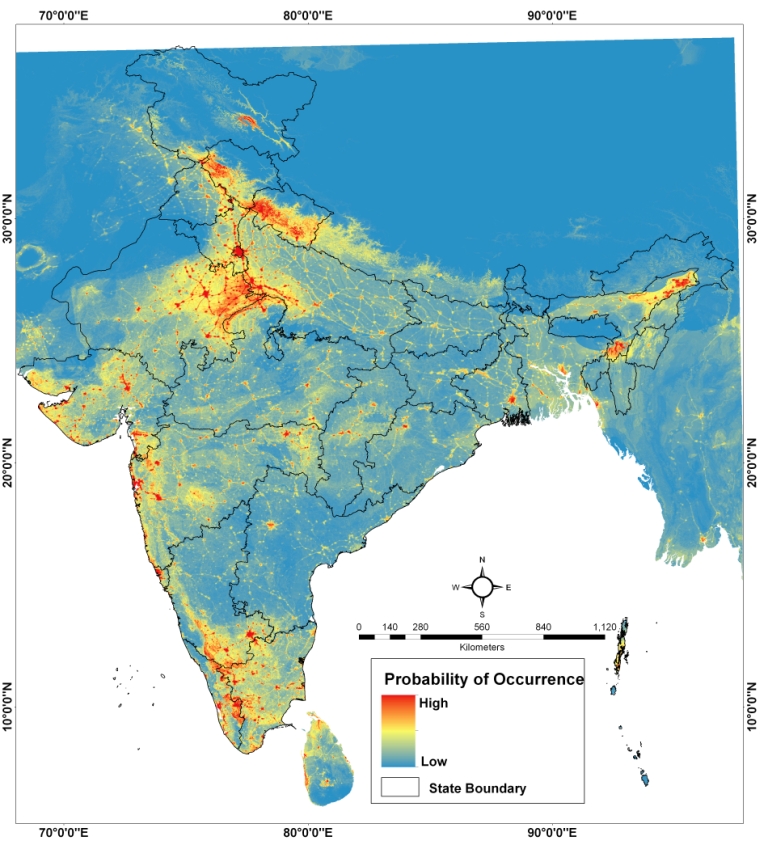
Check Sparrow distribution map (Credit: Saini, WII);
Article by Arpita Bhagat



Last five years sparrows data in India